What Is Esophageal Atresia?
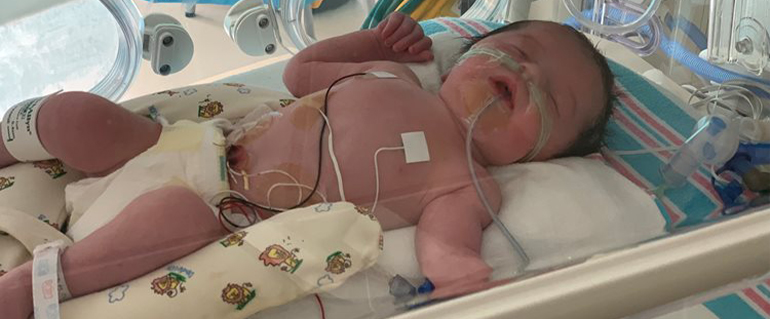
Esophageal atresia is a congenital disorder in which the esophagus does not develop properly. It is a rare condition that occurs when the esophagus does not develop from the stomach, which means it doesn’t have a proper passageway to allow food to move through it. This leads to multiple complications, including difficulty breathing and swallowing food and water.
Children with esophageal atresia are often diagnosed in the first few weeks of life due to the lack of functioning esophagus. Symptoms most commonly include feeding problems, vomiting, weight loss, and apnea Surgical procedures such as a tracheostomy and gastrostomy tube are sometimes required to open up the airway. and allow the child to breath.
What are the Risks & Complications of an Esophageal atresia with a Baby?
The risk of complications for an infant with esophageal atresia include pneumonia, respiratory failure, and sudden death. These complications can also lead to comorbidities such as developmental delays and cognitive impairment. Esophageal atresia is a rare congenital condition in which the esophagus does not connect to the stomach. It is usually associated with other defects, such as an abnormal heart, lungs, or kidneys.
The risk of complications for an infant with esophageal atresia include pneumonia, respiratory failure, and sudden death. There is a syndrome of congenital anomalies associated with esophageal atresia, which includes a heart defect, other abnormalities of the lungs or kidneys, and other anomalies.
There are several different types of esophageal atresia that are defined by the positioning or lack-of-positioning of anatomy. For example:
- Patients with Type I are not positioned in the esophagus, they have no heart defect, and they have normal lungs and kidneys.
- Type II is positioned in the esophagus but has a heart defect or pulmonary atresia.
- Type III is completely lacking all but the cardia of the esophagus. Patients with this type can potentially survive but may require a tracheotomy for air exchange.
- Type IV has a complete absence of esophageal tissue, including both the cardia and all distal esophageal segments. These patients are likely to die soon after birth.
The diagnosis for “esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula” is usually done through an ultrasound, which may reveal a fluid-filled tube in the chest that bridges the mouth and lungs and provides a direct connection between the chest cavity and throat. Further diagnostic testing is necessary to determine whether there are any other anatomic abnormalities present, such as cardiac defects or pulmonary atresia.
Pregnancy and the Risk of Esophageal Atresia in Infants-
Esophageal atresia is a rare condition in which the esophagus does not develop properly, causing it to be blocked by the stomach. The risk of this condition increases with every pregnancy, but there are some steps that can be taken to reduce this risk. Most importantly, pregnant mothers should not smoke or drink alcohol. Smoking is known to decrease the strength of the muscles and ligaments in the esophagus, which can result in a weaker barrier keeping food and stomach contents from going down into the stomach. This condition can also be caused by medications like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Pregnant women who are on these types of drugs should speak with their doctor about carefully monitoring their use during pregnancy.
Symptoms of esophageal atresia vary from baby to baby and may include: difficulty feeding or swallowing, a cough that does not improve with coughing, excessive spitting up or drooling, and frequent vomiting (even after eating).
What you Need to Know about Treatment Options for an Esophageal Atresia in Infant?
Esophageal Atresia is one of the rarest and most complex congenital heart defects. It can cause serious complications during pregnancy and birth, which could lead to death in the newborn. An Esophageal Atresia occurs when a piece of the esophagus fails to develop properly, usually during development in the first trimester. This condition can be diagnosed by ultrasound or echocardiogram. In some cases, surgery may be required to correct this condition. There are two options for treatment: repair or palliation. Repair means that an infant will have surgery to reroute the esophagus through another part of his body and then reconnect it back with the stomach. Palliation means that an infant will have surgery to make sure he has a normal life expectancy while he waits for his esophagus to grow back on its own over time, which could take up to six months or more depending on how old he is at diagnosis.
The first sign of an Esophageal Atresia occurs when there is a buildup of fluid in the lungs. It can be difficult to tell if the child has this condition because it is caused by the intestines and not the heart. Signs that a child may have an Esophageal Atresia include a low weight gain, weakness, lack of appetite, and apnea. Infants are often diagnosed through ultrasound or echocardiogram tests when they are around three months old. If a child is diagnosed with Esophageal Atresia, doctors will perform surgery to remove the blockage. The surgical procedure will create a new opening from the stomach to the esophagus. If it is not discovered in time, this condition can cause pneumonia or death.
When to Contact a Medical Professional about an Esophageal Atresia-
An infant experiencing severe symptoms of an esophageal atresia should be evaluated by a doctor. These include: Severe coughing which sometimes leads to choking, especially when feeding or drinking liquids. This is known as the “choking crisis.” Chest x-ray may demonstrate a large airway obstruction that has resulted in severe respiratory distress. There may also be signs of deterioration in the oxygen saturation levels on the chest x-ray. A baby with a severely blocked esophagus may experience difficulty feeding and swallowing, and the baby may develop anemia. In other cases, babies will be able to feed or drink without any problems. . It is still advised that a doctor be consulted if the infant is experiencing severe symptoms.